POS or point-of-sale systems are commonly observed at retail establishments, restaurants, and other venues. Furthermore, you may have pondered the precise definition of a POS system. What is the purpose of acquiring it for your organization, and what is the mechanism behind its functioning?
What is a POS System?
A point of sale software is a digital cash register that allows retailers to handle payments and record transactions. The software encompasses order tracking, payment processing, inventory monitoring, trend analysis, invoice generation, and marketing data collection. POS technology encompasses countertop terminals and applications that enable customers to process payments using interconnected devices such as smartphones. A Point of Sale (POS) can manifest as physical equipment within a physical establishment or a virtual terminal within an online retail platform. It establishes connections with inventory management, data on sales, and accounting systems. POS functionalities can enhance manufacturers’ operational efficiency and ensure customer and employee satisfaction. Transactions can occur in physical locations or via the internet, creating receipts in either printed or digital format.
Key Components of POS
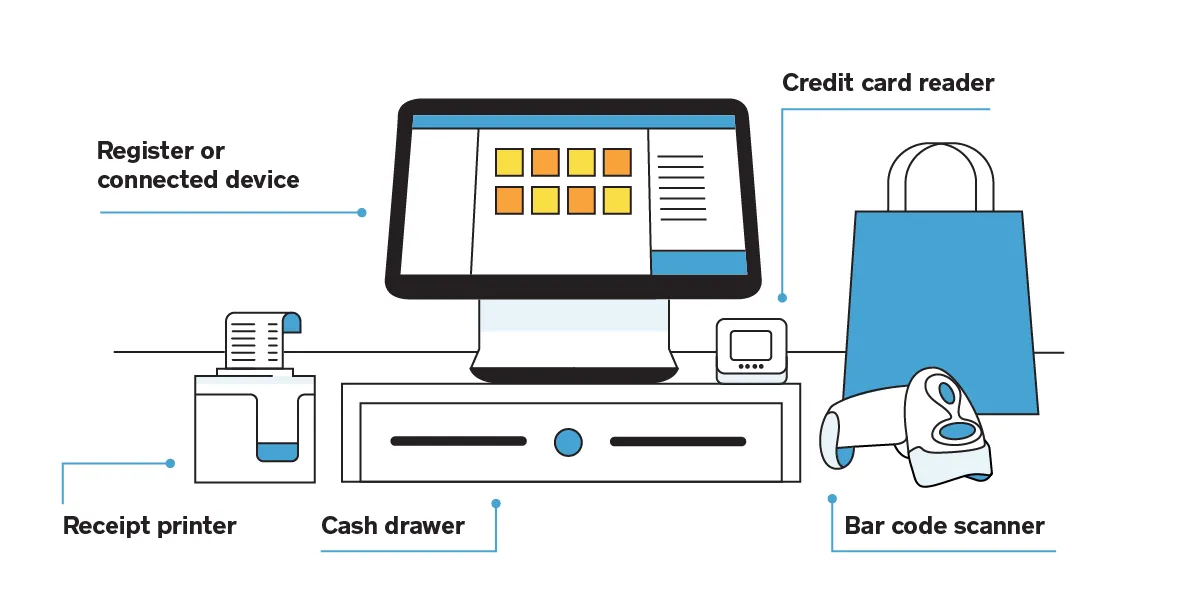
A point of sale (POS) system comprises two primary components: hardware and software. The hardware components include the display screen, cash drawer, payment terminal, barcode scanner, and receipt printer. The display and payment terminal are crucial elements of every POS system. The POS accounting software has functionalities such as a sales interface, inventory control, managing client relationships, and reporting and analysis capabilities. The software’s appearance, sensation, and operational capabilities may differ among providers. Still, most modern systems will include functionalities such as managing inventory, handling client relationships, data analysis and reporting. While not all point of sale (POS) systems necessitate every device, they are vital for firms that engage in credit card transactions or conduct mobile operations.
How Does the POS System Work?
A point-of-sale Software is a technology that facilitates businesses in receiving payments from clients and monitoring sales. Depending upon the arrangement, It applies in both virtual and physical establishments. Contemporary online accounting software is technologically advanced, enabling businesses to process consumer transactions from any location using a POS application and a device with internet connectivity.
The point of sale (POS) system operates in the following manner:
1. A consumer decides to purchase your goods or services. A sales associate can use a barcode scanner or a camera to scan merchandise within a brick-and-mortar establishment. This phenomenon occurs in e-commerce platforms when a customer selects products and proceeds to the checkout process by adding them to their virtual shopping cart and clicking the designated button.
2. The point of sale (POS) software determines the item’s price, which includes any Goods and Services Tax , and eventually adjusts the inventory count to reflect the item’s sale.
3. The consumer makes a payment using several methods, such as credit or debit cards, mobile payments, reward points, gift cards, or cash. The transaction requires authorization from the customer’s bank.
4. The point-of-sale transaction is completed, enabling the business to ship or deliver the purchased items. This technique is crucial for firms to oversee their sales and customer engagements efficiently.
Benefits of a Point of Sale System
POS software provides numerous advantages to retail businesses. These are some of the most crucial:
Improved Efficiency: Optimizes sales procedures, resulting in shorter checkout times and reduced errors
Inventory Management: Facilitates immediate monitoring of stock levels to ensure prompt reordering and minimize occurrences of stockouts or overstocking.
Comprehensive Reporting: Produces detailed reports on sales, inventory, and consumer behavior to assist firms in optimizing their merchandising and marketing strategies.
Customer Insights: Acquires useful purchase trends and preferences data to facilitate targeted marketing efforts and customized customer experiences.
Integration Capabilities: Effortlessly interfaces with other business systems, including accounting software, e-commerce sites and client relationship management (CRM) tools.
Enhanced Security: Protecting confidential client data and minimizing the possibility of fraudulent activities by utilizing encryption and adhering to the laws set by PCI DSS.