Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a prevalent issue affecting millions of people worldwide. Often misunderstood, it can lead to severe oral health problems, including exposed tooth roots.
If left unattended, the repercussions could be significant. It could impact not just your oral health but your overall well-being.
So in this listicle, we’ll unpack the relationship between gum disease and exposed tooth roots. We’ll provide you with vital insights and actionable advice.
Let’s dive in!
Understanding Gum Disease
Gum disease is an inflammatory ailment mainly brought on by oral bacterial infections. Gingivitis is the initial condition, marked by red, swollen, and readily bleeding gums.
If left untreated, it can escalate to periodontitis. This is a more severe form that affects the bone and tissues supporting the teeth.
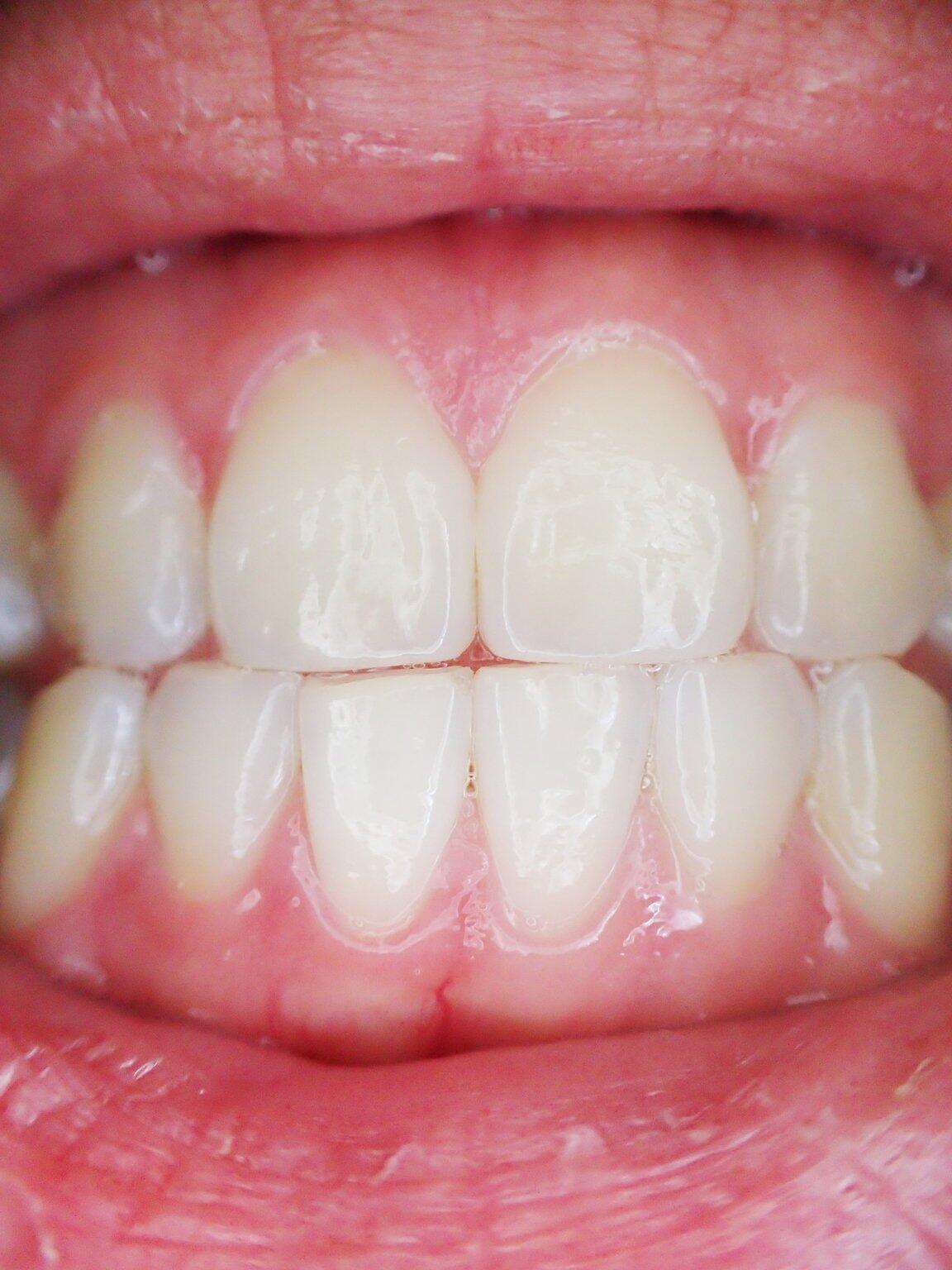
One of the most alarming consequences of advanced gum disease is the exposure of tooth roots. This can lead to heightened sensitivity and other complications.
Research indicates that nearly half of adults aged 30 and older have some form of gum disease. This makes it crucial to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Proper oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and early intervention is important. They can reduce the risk of developing severe gum disease.
How Gum Disease Leads to Bone Loss
One of the critical aspects of gum disease is bone loss. Periodontitis triggers an immune response that leads to the destruction of the bone tissue supporting the teeth.
As the bone deteriorates, the gums begin to recede, exposing the tooth roots. This process not only affects the stability of the teeth. It also makes the exposed roots more susceptible to decay and infection.
Individuals with severe periodontitis are more likely to experience bone loss compared to those with milder forms of the disease. That’s why early detection and treatment is crucial. They can prevent bone deterioration and maintain oral health.
The Role of Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections play a pivotal role in the development and progression of gum disease. The mouth harbors a myriad of bacteria, some of which form plaque on the teeth.
If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can harden into tartar, providing a breeding ground for harmful bacteria. These bacteria release toxins that irritate the gums, leading to inflammation, infection, and eventually, gum disease.
How to Mitigate Bone Loss and Exposed Roots
There are ways to mitigate bone loss before it becomes serious. Here are just some of the things you can do at home:
Brush and Floss Daily
Aim to brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Use gentle, circular motions and avoid aggressive scrubbing as it can damage the gums. Additionally, flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth.
Use Antibacterial Mouthwash
Using an antiseptic mouthwash after brushing and flossing can help reduce bacteria in the mouth. This helps prevent plaque buildup, which can contribute to gum disease.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing gum disease and bone loss. It weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and heal damaged tissue.
Smoking also triggers inflammation and restricts blood flow, making it harder for the gums to heal. Quitting smoking can improve your overall health and reduce the risk of complications from gum disease.
Eat a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for maintaining healthy gums and bones. Vitamin C, in particular, plays a crucial role in gum health and can help prevent gum disease.
Start eating more fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, and limit your intake of sugary and acidic foods. This can contribute to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease.
Use Antimicrobial Mouthwash
If you have severe periodontitis or are at high risk for gum disease, your dentist may recommend using an antimicrobial mouthwash. These contain active ingredients that can help reduce harmful bacteria and promote healing.
Get Regular Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to monitor your oral health and identify any signs of gum disease or bone loss early on. They can also provide professional cleaning to remove tartar buildup that cannot be removed by brushing alone.
Consider Using a Water Flosser
In addition to traditional flossing, a water flosser can help in reaching areas that might be missed, especially if you have braces, bridges, or dental implants. The pulsating water helps to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and just below the gumline, reducing the risk of inflammation and infection.
Manage Stress Levels
Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight off infections, including those in your gums. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as exercise, meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises to help keep your immune system strong and your gums healthy.
Avoid Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding or clenching, known as bruxism, can not only wear down the enamel but also exacerbate gum recession and bone loss. If you grind your teeth, consider wearing a night guard to protect them and consult with your dentist for other potential remedies.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps in keeping your mouth hydrated and encourages the production of saliva, which naturally cleanses the mouth. Saliva helps dilute acids produced by bacteria in plaque and wash away food particles that could contribute to gum disease.
Be Mindful of Medications
Certain medications can affect your oral health, leading to dry mouth and gum swelling. If you’re taking medications regularly, consult your healthcare provider or dentist to understand how they may impact your gums, and explore possible alternatives or solutions.
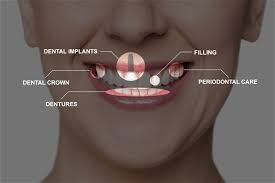
Treatment Options for Gum Disease and Exposed Tooth Roots
If you have been diagnosed with gum disease and exposed tooth roots, your dentist may recommend one or more of the following treatment options:
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling involves removing plaques and tartar from above and below the gum line. Root planing smooths out rough spots on the root surface to prevent bacteria from gathering and causing further damage.
Antibiotics
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control bacterial infections in the gums. They can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected area.
Gum Graft Surgery
If there is a significant gum recession, your dentist may recommend gum graft surgery. This involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth and placing it over the exposed tooth roots to protect them.
When it comes to gum grating, there are also different kinds of gum recession treatment options. Traditional grafting involves taking tissue from the roof of your mouth and placing it over the exposed tooth root. Alternatively, there are also less invasive options, such as pinhole surgery or platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) therapy.
Nowadays, there is also Chao Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST) that is minimally invasive and can be done in one visit. This technique involves making a small hole above the affected tooth and using specialized instruments to loosen the gum tissue and reposition it over the exposed root.
Dental Implants
In severe cases where teeth have been lost due to advanced gum disease, dental implants may be an option. These are artificial tooth roots that are surgically placed into the jawbone and topped with a crown.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a modern treatment option for gum disease that targets infected gum tissue. By using focused light to selectively remove inflamed areas, laser therapy helps reduce bacteria in the gums while minimizing bleeding and discomfort. It’s less invasive than traditional methods and can promote faster healing.
Bone Grafting
For patients who have experienced significant bone loss, bone grafting might be a viable option. This procedure involves transplanting bone tissue to regenerate lost bone around the teeth. By providing scaffolding for new bone growth, bone grafting can help restore stability to affected teeth and prevent further gum recession.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) is a technique used during periodontal surgery to encourage the growth of new bone and gum tissue. A specialized membrane is placed between the bone and gum tissue to prevent unwanted tissue from occupying the area and to allow the bone and gum tissue to regenerate.
Enamel Matrix Derivative Application
The application of enamel matrix derivative proteins is another technique in periodontal therapy. These proteins can stimulate the regrowth of hard and soft tissue around teeth, helping to restore areas affected by gum disease.
This treatment has been shown to aid in improving attachment levels around teeth. It may be used in conjunction with other periodontal procedures.
Exposed Tooth Roots Are a Sign of Severe Gum Disease
Exposed tooth roots are a warning sign that gum disease has progressed to a severe stage. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups can prevent this from happening.
If you notice signs of gum recession or have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, speak to your dentist about potential treatment options. With early intervention, you can save your teeth and maintain optimal oral health. Remember, prevention is always better than cure! So make sure to take care of your gums for a lifetime of smiles.
Was this article helpful? If so, check out the rest of our site for more.