Conrad Peutinger ii 1475; When considering the Renaissance, prominent figures such as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo typically come to mind. However, another significant yet often overlooked individual who played a crucial role during this transformative period is conrad peutinger ii 1475, born in 1475.
In this exploration, we delve into the life and lasting influence of Conrad Peutinger II, examining how his scholarly work and dedication to preserving historical knowledge continue to resonate today. By studying his impact, we gain a deeper appreciation for the breadth of intellectual achievements that characterized the Renaissance and the enduring legacy of those who contributed to it.
Overview of Conrad Peutinger II and the Peutinger Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Conrad Peutinger II |
| Birthdate | October 14, 1475 |
| Field | Humanist Scholar, Cartographer, Diplomat |
| Notable Work | Peutinger Table (Tabula Peutingeriana) |
| Description of the Map | An ancient Roman road map depicting extensive road networks across Europe and parts of Asia. |
| Initial Purpose | Navigation and trade route planning for travelers and merchants |
| Current Location | Austrian National Library, Vienna |
| Significance | Provides historical insights into Roman geography and cultural exchanges |
| Controversies | Accuracy debates and ownership disputes over the centuries |
| Legacy | Continues to influence historical and cartographic studies |
The Early Life and Scholarly Pursuits of Conrad Peutinger ii 1475

conrad peutinger ii 1475, born on October 14, 1475, in Augsburg, Germany, emerged from a privileged and influential background that afforded him exceptional educational opportunities. Initially focusing on law at the universities of Basel and Padua, Peutinger’s interests soon expanded beyond the legal field. His intellectual curiosity spanned history, geography, and classical antiquity, areas that would come to define his scholarly achievements.
As a leading figure in the humanist movement—a cultural renaissance aimed at reviving the art, literature, and philosophy of ancient Greece and Rome—Peutinger’s commitment to antiquity was unmistakable. His dedication was reflected in his impressive collection of ancient manuscripts, coins, and artifacts. This collection evolved into one of the most significant private libraries of the Renaissance, underscoring his pivotal role in the preservation and study of classical knowledge.
The Konrad Peutinger ii 1475: A Renaissance Milestone
The Konrad Peutinger ii 1475, crafted in 1475, stands as a significant artifact from the late 15th century, offering an early depiction of Europe and parts of Asia. This remarkable map, created during the Renaissance, reflects a growing curiosity about geography and exploration. As scholars of the time strived to expand their understanding of the world, cartography saw remarkable advancements.
Conrad Peutinger was more than a cartographer; he was a humanist scholar dedicated to merging ancient knowledge with contemporary insights. His work exemplified the Renaissance spirit of reviving classical wisdom and applying it to modern contexts. The Peutinger map was not just a navigational tool but also a detailed record of cultural and economic interactions between regions. Its comprehensive portrayal of cities and trade routes provided invaluable information for travelers and merchants, highlighting the interconnectedness of different parts of the world.
This period marked a pivotal moment in the evolution of mapping practices, laying the groundwork for the sophisticated cartographic techniques that we use today. The conrad peutinger ii 1475 remains a testament to the era’s commitment to exploration and knowledge.
Conrad Peutinger ii 1475: Scholar, Diplomat, and Influencer
conrad peutinger ii 1475 impact extended beyond his scholarly pursuits into the realms of diplomacy and politics. As a city councilor in Augsburg and a representative of the Holy Roman Empire on various diplomatic missions, Peutinger played a significant role in shaping the political and cultural landscape of his time. His involvement in these areas helped propagate humanist ideals across Europe, bridging intellectual and political spheres.
Peutinger’s dual contributions as a scholar and diplomat had a profound effect on the Renaissance understanding of the world. His dedication to preserving ancient texts and his innovative work in cartography, exemplified by the Peutinger Table, provided new insights into geography and history. This influential map, along with his preservation efforts, helped future scholars and explorers better comprehend the world, leaving a lasting legacy that shaped Renaissance views on geography and historical knowledge.
The Story of the Conrad Peutinger ii 1475: From Creation to Controversy
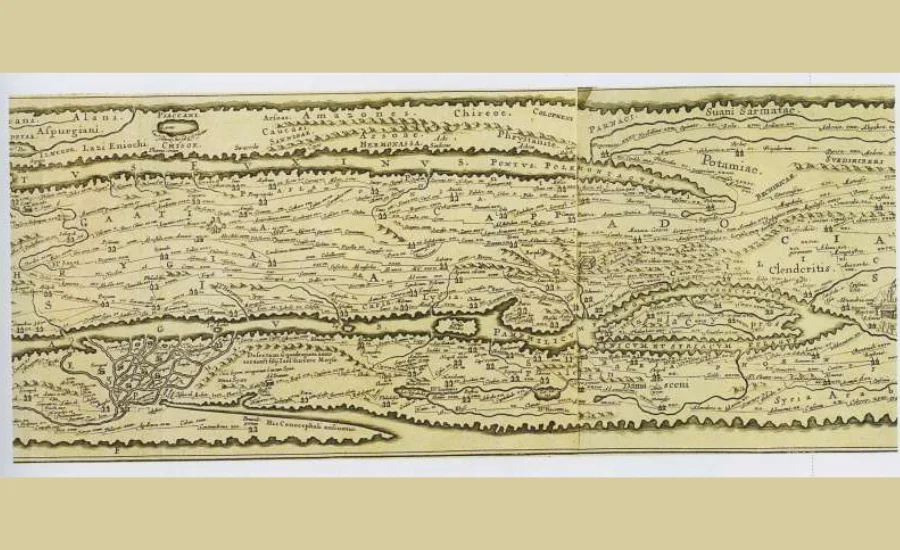

The conrad peutinger ii 1475 tells a story as captivating as the map itself. Created by the scholar and humanist Conrad Peutinger, this historical artifact was designed to illustrate the extensive network of ancient Roman roads. Initially, the map served a practical function, aiding travelers and merchants in navigating Europe during an era when communication was often challenging.
As time passed, the map changed hands multiple times, each owner playing a role in preserving its historical significance through wars and political shifts. This journey through history has added layers to its story, turning it into more than just a navigational tool. The map has become a symbol of Renaissance intellectual pursuit and exploration.
Today, the conrad peutinger ii 1475 is housed at the Austrian National Library in Vienna. This prestigious institution, renowned for its extensive collection of historical documents, provides an ideal setting for such an important artifact. The map continues to attract scholars and historians who study its detailed portrayal of ancient Roman geography.
Despite its revered status, the map has sparked debates among historians and cartographers. Some question the accuracy of its geographical features and the methods used in its creation. Discrepancies between Peutinger’s renderings and modern geographical understanding have led to discussions about the map’s reliability as a historical document.
Ownership disputes have also complicated the map’s legacy. Its multiple transfers over the centuries have led to conflicts over rightful possession, sometimes overshadowing its artistic and historical value. Additionally, there are ongoing debates about how the map represents cultural aspects of ancient Rome, with some scholars arguing that it omits significant details.
These controversies underscore the complexities surrounding this remarkable artifact, highlighting both its contributions to our understanding of historical geography and the challenges of interpreting its significance.
The Legacy of the Peutinger Table
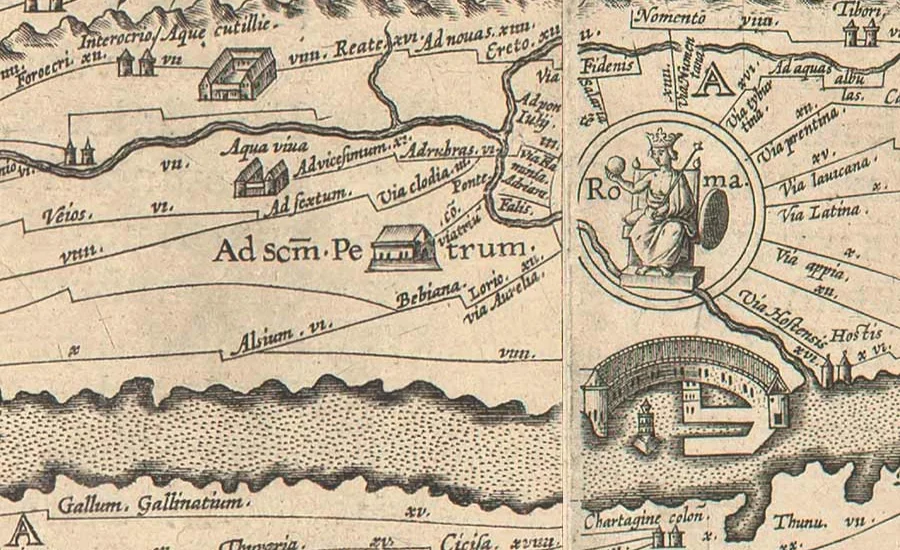
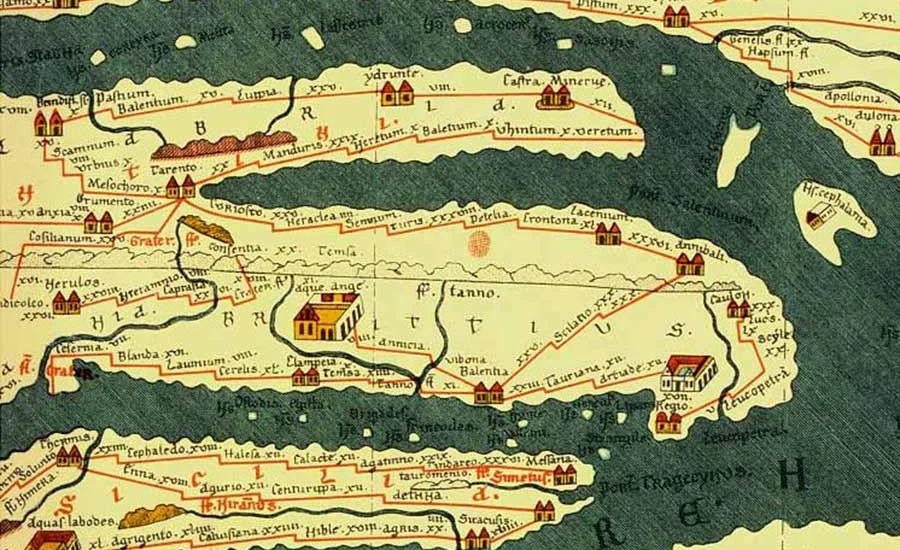
Among Conrad Peutinger ii 1475 many scholarly contributions, the “Tabula Peutingeriana,” commonly known as the Peutinger Table, stands out as a significant achievement. This ancient Roman map, inherited by Peutinger from a friend, is one of the earliest surviving examples of a road map, offering a unique perspective on Roman geography and travel.
The Peutinger Table is an impressive artifact, extending over 22 feet when fully unrolled. It illustrates the extensive network of roads that spanned the Roman Empire, from the western reaches of Britain to the eastern frontiers of India. The map is remarkable not only for its historical value but also for its detailed representation of towns, cities, and the distances between them. This extensive and detailed depiction made the map an essential guide for Roman travelers and traders, and it remains an invaluable resource for historians studying the ancient world today.
Contributions to the Preservation of Ancient Texts
Conrad Peutinger ii 1475 influence extended far beyond his achievements in cartography. His work in the preservation of ancient texts was equally pivotal during the Renaissance, a period marked by the rediscovery of long-forgotten works from antiquity. Peutinger was a key figure in this scholarly revival, playing a crucial role in safeguarding and revitalizing classical literature.
As a dedicated patron of scholars and a collector of rare manuscripts, Peutinger significantly contributed to the preservation and dissemination of ancient knowledge. He was actively involved in transcribing and conserving these invaluable texts, ensuring that key works of classical literature, philosophy, and science were not lost to time. The manuscripts from Peutinger’s collection continue to be of great importance in the academic world, reflecting his enduring impact on the study and preservation of ancient intellectual heritage.
Conrad Peutinger II, born in 1475, was a pivotal figure in Renaissance scholarship whose contributions to cartography and historical preservation continue to resonate today. His creation, the Peutinger Table, stands as a testament to the era’s burgeoning interest in geography and exploration. This ancient Roman map, with its intricate depiction of roads and cities, not only served as a practical guide for travelers and merchants but also encapsulated the intellectual spirit of the time.
Final Words
Over the centuries, the Peutinger Table has been meticulously preserved and studied, highlighting its significant role in shaping our understanding of ancient geography. Despite controversies and debates regarding its accuracy and ownership, the map remains an invaluable artifact. It offers insights into the cultural and economic exchanges of the Roman Empire and reflects the Renaissance’s drive for knowledge and exploration.
Today, housed at the Austrian National Library in Vienna, the Peutinger Table continues to be a focal point for scholars and historians, revealing the rich tapestry of history through its detailed representation of ancient roads. Conrad Peutinger II’s legacy endures through this remarkable map, symbolizing the enduring quest for knowledge and historical preservation.
For more information and updates join us on Buzz Revolve