Gout is a painful form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation and intense pain.
While medication can help manage gout symptoms, physical therapy can also play a crucial role in providing gout pain relief and improving overall joint health.
In this guest post, we’ll explore various physical therapy techniques that can help alleviate gout pain and promote healing.
What is Gout?
Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to the formation of crystals in the joints. The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, but gout can also occur in the ankles, heels, knees, wrists, and fingers.
Symptoms of gout include:
- Sudden and severe joint pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Stiffness, etc.
Is Physical Therapy Effective for Gout?
Physical therapy is a safe and effective treatment for gout. Many people with gout report significant improvement in their symptoms after undergoing physical therapy.
What are the Benefits of Physical Therapy for Gout?
There are many benefits to physical therapy for gout. Some of the most important benefits include:
- Reduced pain
- Improved joint function
- Increased mobility
- Improved quality of life, and more.
We’ll now discuss the role of PT in gout management and improved lifestyle in detail.
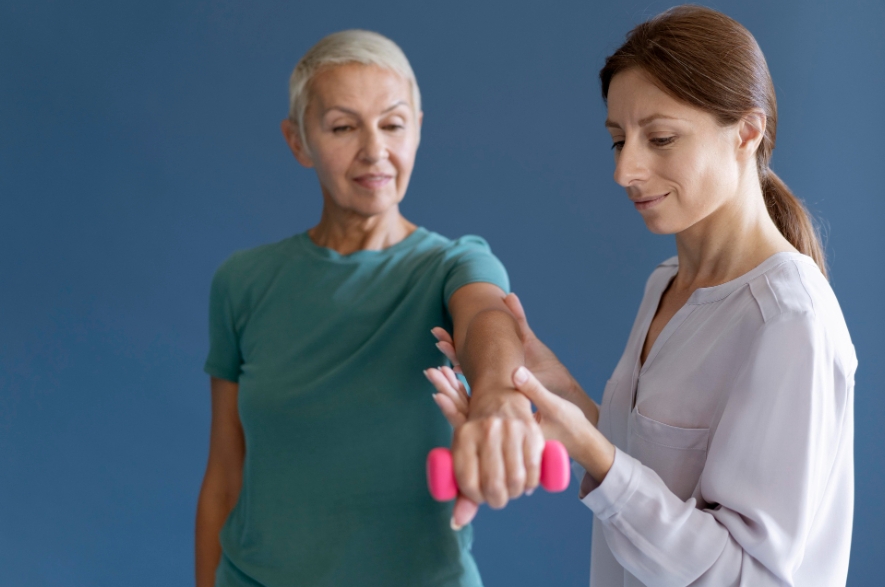
The Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can be an effective treatment for gout, especially during the intercritical phases (the periods between acute attacks). A physical therapist will help reduce inflammation, improve range of motion, and strengthen the affected joint to prevent future attacks.
Here are some of the techniques they may use to heal patients:
1. Reducing Inflammation
Reducing inflammation is a key priority in the management of gout. Physical therapists can use various modalities to achieve this, such as:
- Ultrasound therapy: Uses sound waves to heat deep tissues and increase blood flow, which can help reduce inflammation.
- Laser therapy: Low-level laser therapy can help decrease pain and inflammation in the affected joint.
- Electric muscle stimulation: Sends mild electrical impulses to the affected area, which can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Ice and heat therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected joint can help reduce inflammation and pain during acute attacks, while heat therapy can be beneficial during the intercritical phases.
2. Improving Range of Motion
Once the acute inflammation has been addressed, the focus shifts to improving the range of motion of the affected joint. Physical therapists use manual techniques, such as joint mobilization and massage, to increase flexibility and reduce stiffness.
3. Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the muscles around the affected joint can help support and stabilize it, reducing the risk of future attacks. Physical therapists may prescribe specific exercises to target the affected area, such as:
Resistance band exercises: Using resistance bands to perform exercises that target the muscles around the affected joint.
Weight-bearing exercises: Low-impact exercises, such as walking or using an elliptical machine, can help strengthen the joint while minimizing stress.
4. Gait Training and Assistive Devices
If the gout is affecting the lower extremities, physical therapists may work on gait training to help the patient walk more efficiently and reduce stress on the affected joint. They may also recommend the use of assistive devices, such as canes or walkers, to provide additional support and stability.
5. Education and Lifestyle Modifications
Physical therapists can provide education on the importance of maintaining a healthy weight, staying hydrated, and avoiding foods high in purines (such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol) to help prevent future gout attacks. They can also offer advice on appropriate footwear and the use of orthotics to provide additional support and cushioning for the affected joint.
Gout in the Shoulder (Shoulder Gout)
While gout most commonly affects the lower extremities, it can also occur in the shoulder joint. Gout in the shoulder is less common than gout in other joints, but it can be just as painful and debilitating.
Physical therapy for shoulder gout may include techniques such as:
- Cryotherapy: Applying ice packs to the affected shoulder can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Ultrasound therapy: Can help increase blood flow and reduce inflammation in the shoulder joint.
- Stretching and range-of-motion exercises: Gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises can help maintain flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises: Specific exercises to target the rotator cuff muscles and improve shoulder stability.
What Can I Expect From Physical Therapy for Gout?
If you are considering physical therapy for gout, you can expect to work closely with a physical therapist to develop a personalized treatment plan. The treatment plan will be tailored to your specific needs and goals. You may also need to make some lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or avoiding foods that trigger gout attacks.
How Long Does Physical Therapy Take for Gout?
The length of physical therapy for gout varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s goals. Most people with gout see improvement within a few weeks of starting physical therapy. However, some people may need to continue physical therapy for several months or even years.
Wrapping Up
Physical therapy offers a comprehensive approach to managing gout, providing relief from gout pain and improving overall joint health.
By employing a combination of techniques, including inflammation-reducing therapies, range-of-motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and lifestyle modifications, physical therapists can assist patients in achieving better outcomes and reducing the likelihood of future gout attacks.
If you’re experiencing gout pain, consider consulting a qualified physical therapist to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.