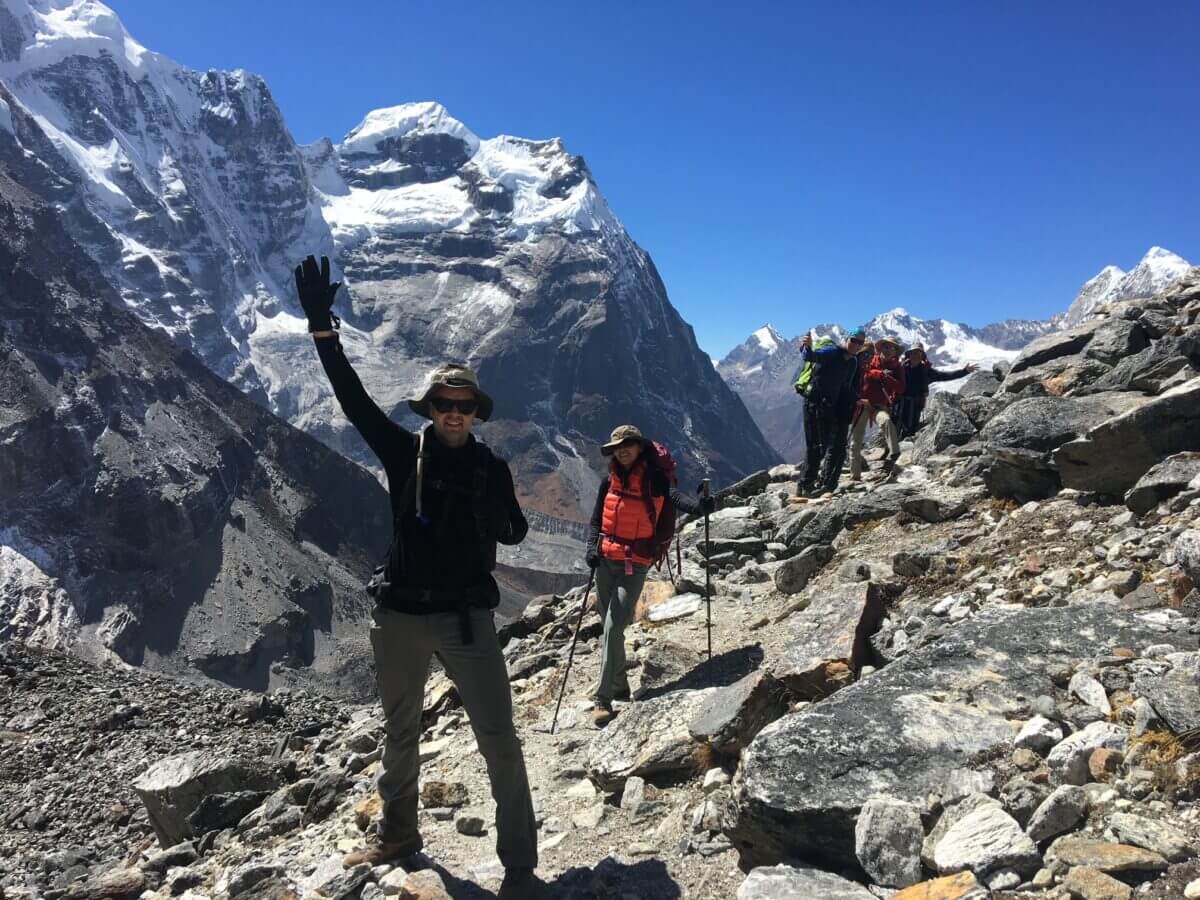
Trekking and climbing Mera Peak, standing at 6,476 meters (21,247 feet) in the remote Khumbu region of Nepal, offers breathtaking vistas and a challenging adventure. To ensure a safe and enjoyable experience, it’s crucial to prioritize health and safety throughout the journey. Here are essential tips to consider:
Before embarking on the trek to Mera Peak, adequate physical preparation is essential. Focus on cardiovascular fitness to improve endurance, as trekking involves long hours of walking uphill and downhill. Strength training for the legs, core, and upper body helps with stability and carrying a backpack. Flexibility exercises reduce the risk of muscle strains and improve agility on uneven terrain. Aim to start your training regimen at least 3-6 months before the trek, gradually increasing intensity and duration to simulate the demands of high-altitude trekking.
Acclimatization is critical to avoid altitude sickness, which can occur when ascending to higher altitudes too quickly. Plan your itinerary with gradual ascents and rest days to allow your body time to adjust. It’s recommended to climb high during the day and sleep at a lower altitude to aid acclimatization—a strategy known as “climb high, sleep low.” Stay hydrated and avoid alcohol and tobacco, as they can worsen altitude symptoms. Familiarize yourself with the signs of altitude sickness, such as headaches, nausea, and dizziness, and descend immediately if symptoms worsen.
Maintain a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats to sustain energy levels during the trek. Pack lightweight, high-energy snacks such as nuts, dried fruits, and energy bars for quick refueling on the trail. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids throughout the day, even if you don’t feel thirsty, to prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate altitude-related symptoms.
Invest in high-quality trekking gear and equipment suitable for variable weather conditions. Essential items include a sturdy backpack, waterproof clothing, sturdy trekking boots with ankle support, and a reliable sleeping bag rated for cold temperatures. Carry a comprehensive first aid kit with medications for altitude sickness, pain relief, and common ailments. A headlamp, trekking poles, and a portable water purification system are also essential.
Travel with an experienced guide or in a guided group familiar with the region and its challenges. Register with local authorities and obtain necessary permits before starting the trek. Follow safety protocols, such as staying on marked trails and respecting local customs and wildlife. In case of emergencies, carry a communication device such as a satellite phone or personal locator beacon (PLB) to call for help.
Practice Leave No Trace principles by packing out all waste and minimizing your impact on the environment. Respect local customs and traditions, including dress codes and behavior around sacred sites. Be mindful of wildlife and avoid disturbing natural habitats.
By prioritizing health and safety throughout your trek to Mera Peak, you can maximize enjoyment while minimizing risks, ensuring a memorable and rewarding adventure in the Himalayas.
Introduction to Health and Safety in Trekking
Health and safety are paramount considerations when embarking on trekking adventures, especially in remote and high-altitude environments like those encountered while trekking to peaks such as Mera Peak in Nepal. Ensuring physical preparedness, understanding potential hazards, and adhering to safety protocols are essential for a safe and enjoyable trekking experience.
Understanding Altitude Sickness: Symptoms and Causes
Altitude sickness, also known as acute mountain sickness (AMS), occurs when ascending to high altitudes too quickly without proper acclimatization. Symptoms typically include headaches, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping. The primary cause is reduced oxygen levels and lower air pressure at higher altitudes, leading to fluid leakage from blood vessels into the brain or lungs in severe cases.
Preventive Measures for Altitude Sickness
Preventing altitude sickness involves gradual ascent and proper acclimatization. Plan your itinerary with incremental altitude gains and incorporate rest days to allow your body to adjust. Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids and avoid alcohol and tobacco, which can exacerbate symptoms. Consider medications like acetazolamide (Diamox) to help prevent altitude sickness, especially if prone to severe symptoms. Recognize early signs of AMS and descend to lower altitudes if symptoms worsen, as rapid descent is the most effective treatment.
Essential Warm-Up Exercises
Warm-up exercises are crucial before trekking to prepare muscles and joints for physical activity and reduce the risk of injuries. Start with light aerobic activities like walking or gentle jogging to increase heart rate and blood flow to muscles. Dynamic stretches such as leg swings, arm circles, and lunges improve flexibility and range of motion. Incorporate exercises specific to trekking, such as squats and calf raises, to strengthen leg muscles used during uphill climbs. Gradually increase intensity and duration of warm-up exercises as fitness levels improve, ensuring readiness for the physical demands of trekking at higher altitudes.
Hydration: Importance and Recommendations
Hydration is crucial during trekking, especially in high-altitude environments like Mera Peak where dehydration can exacerbate altitude sickness. Adequate fluid intake helps maintain bodily functions, regulate body temperature, and support muscle function. Drink water regularly throughout the day, even if not feeling thirsty, and consider electrolyte-replenishing drinks to maintain proper hydration levels. Monitor urine color; clear or light yellow urine indicates adequate hydration.
Nutrition Guidelines During the Trek
Proper nutrition is essential for sustaining energy levels and supporting physical exertion during trekking. Focus on a balanced diet rich in carbohydrates for energy, proteins for muscle repair, and fats for sustained energy release. Pack lightweight, nutrient-dense snacks such as nuts, dried fruits, energy bars, and trail mix for quick and easy consumption on the trail. Include regular meals with a variety of foods to meet nutritional needs. Consider dietary preferences and any special dietary requirements when planning meals.
Proper Clothing and Gear Selection
Choosing the right clothing and gear is crucial for comfort, safety, and protection from varying weather conditions encountered while trekking to Mera Peak. Layer clothing to adjust for changing temperatures and weather conditions; include moisture-wicking base layers, insulating mid-layers, and waterproof outer layers. Invest in sturdy trekking boots with ankle support and proper traction for varied terrain. Pack essentials like a warm hat, gloves, sunglasses, sunscreen, and a hat with a brim for sun protection. A comfortable and well-fitted backpack with a rain cover is essential for carrying gear and supplies.
Weather Considerations and Preparedness
Weather conditions in the Himalayas, including those around Mera Peak, can be unpredictable and vary throughout the day. Monitor weather forecasts before and during the trek to anticipate changes and plan accordingly. Be prepared for cold temperatures, strong winds, and potential precipitation by packing appropriate clothing and gear. Carry a waterproof jacket, pants, and extra layers to stay warm and dry. Maintain awareness of weather patterns and heed local advice or warnings to ensure safety while trekking in mountainous terrain.
Emergency Procedures in Remote Locations
When trekking in remote locations like Mera Peak Expedition, being prepared for emergencies is crucial for ensuring safety. Familiarize yourself with local emergency contacts and communication options, such as satellite phones or emergency beacons. Have a clear plan for emergency evacuation, including designated meeting points and routes. Carry a comprehensive first aid kit and know how to administer basic first aid for common injuries and illnesses. Stay informed about potential hazards and weather conditions, and make decisions based on safety considerations rather than summit objectives.
First Aid Kit Essentials for Trekking
A well-stocked first aid kit is essential for addressing minor injuries and managing medical emergencies while trekking. Essentials include adhesive bandages, gauze pads, adhesive tape, antiseptic wipes, tweezers, scissors, pain relievers (like ibuprofen or acetaminophen), blister treatment (moleskin or blister pads), and medications for common ailments like diarrhea and allergies. Include personal medications and prescriptions specific to individual needs. Consider carrying a CPR mask, a thermometer, and a splint for more serious injuries. Regularly check and replenish the first aid kit before each trekking adventure.
Maintaining Mental Health During the Climb
Maintaining mental health is crucial during challenging climbs like Mera Peak, where physical exertion and altitude can impact emotional well-being. Practice mindfulness and relaxation techniques to manage stress and anxiety. Set realistic goals and celebrate achievements along the way to boost morale. Stay connected with fellow trekkers or a supportive trekking group to share experiences and provide mutual encouragement. Be aware of altitude-related mood changes and communicate openly with teammates and guides about feelings or concerns. Prioritize rest and sleep to support mental clarity and emotional resilience throughout the trek.
Choosing the Right Trekking Partner
Choosing the right trekking partner is essential for a safe and enjoyable experience on climbs like Mera Peak. Look for someone with similar fitness levels, trekking experience, and goals. Compatibility in communication and decision-making styles is important for navigating challenges and making joint decisions. Discuss expectations, preferences, and concerns before the trek to ensure compatibility and alignment of goals. Trust and mutual respect are foundational; prioritize safety and support each other during the journey. Consider joining guided trekking groups or connecting with experienced trekking partners through reputable organizations for added safety and camaraderie.
Navigation Skills and Safety Precautions
Navigation skills are critical for safe trekking, especially in remote and challenging terrains like those around Climb Mera Peak. Familiarize yourself with maps, GPS devices, and compass use before setting out. Plan your route in advance, noting landmarks and key waypoints. Stay on marked trails and pay attention to trail markers or cairns. Be prepared to navigate in varying weather conditions, including low visibility due to fog or snow. Practice orienteering and map reading skills to confidently navigate terrain features and avoid getting lost.
Communication Devices and Their Importance
Carrying communication devices is essential for safety and emergency preparedness while trekking in remote areas like Mera Peak. Satellite phones or emergency beacons (PLBs) allow for reliable communication in areas without cell coverage. Register your devices with local authorities and emergency response services before your trek. Maintain batteries and keep devices protected from moisture and extreme temperatures. Test communication devices before the trek to ensure functionality and familiarity with operation in case of emergencies.
Dealing with Wildlife Encounters Safely
Encounters with wildlife can occur while trekking in the wilderness around Mera Peak. Maintain a respectful distance from animals to avoid disturbing natural behaviors or triggering defensive reactions. Research local wildlife and understand their habitats and behaviors. Carry bear spray or other deterrents recommended for the region and know how to use them safely. Store food and scented items securely to prevent attracting wildlife to camp areas. If encountering wildlife, remain calm, avoid sudden movements, and slowly back away while maintaining eye contact.
Understanding Terrain and Hazards
Understanding terrain and potential hazards is crucial for assessing risks and planning safe routes while trekking near Mera Peak. Terrain features such as glaciers, moraines, and rocky slopes require careful navigation and may pose risks of slips, falls, or avalanches. Be aware of changing weather conditions that can affect terrain stability and visibility. Carry appropriate gear like trekking poles for stability and crampons or microspikes for icy surfaces. Stay informed about local hazards such as river crossings, rockfalls, and altitude-related risks. Consult with experienced guides or local authorities for updated information and safety recommendations specific to the trekking season and conditions.
Planning for Weather-Related Emergencies
Weather-related emergencies can pose significant risks while trekking or climbing near Mera Peak. It’s crucial to monitor weather forecasts before and during the trek and be prepared to adjust plans accordingly. Carry appropriate gear for varying weather conditions, including waterproof clothing, extra layers for warmth, and sun protection like sunglasses and sunscreen. In case of unexpected storms or severe weather, seek shelter in designated safe areas or sturdy structures. Communicate your itinerary and emergency contacts with reliable communication devices like satellite phones or emergency beacons (PLBs). Develop a contingency plan for evacuation routes and emergency response procedures, including first aid and CPR training for group members.
Safety Protocols for Glacier Travel
Glacier travel requires careful planning and adherence to safety protocols due to inherent risks such as crevasses, unstable ice, and avalanches. Travel with experienced guides familiar with glacier navigation and rescue techniques. Use proper equipment such as ropes, harnesses, and ice axes for secure travel across glaciers. Maintain a safe distance from crevasse edges and travel in roped teams with sufficient spacing to prevent multiple falls. Carry crevasse rescue gear and practice self-rescue techniques before attempting glacier crossings. Avoid travel during periods of high avalanche risk and be prepared to change routes based on conditions and guidance from local experts.
Post-Climb Health Monitoring
Monitoring your health post-climb is essential for identifying and managing potential altitude-related issues or physical strains. Pay attention to symptoms of altitude sickness such as headaches, nausea, fatigue, and dizziness, which may persist after descent. Rest and hydrate adequately to support recovery and aid in acclimatization. Monitor urine output and color to assess hydration levels. Seek medical attention for persistent symptoms or concerns about altitude-related illnesses like High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE) or High Altitude Cerebral Edema (HACE). Gradually reintroduce physical activity and maintain a balanced diet to promote muscle recovery and overall well-being.
Reflecting on Your Experience: Lessons Learned
Reflecting on your climbing experience near Mera Peak allows for personal growth and future preparation. Evaluate challenges faced during the climb, including physical, mental, and logistical aspects. Identify strengths and areas for improvement in training, equipment, and decision-making. Consider how weather conditions, terrain, and group dynamics influenced the climb’s outcome. Share insights and lessons learned with teammates, guides, or mentors to exchange perspectives and enhance future planning and preparation. Celebrate achievements and milestones reached during the climb, fostering a sense of accomplishment and motivation for future adventures in mountaineering or trekking.