Maintaining reliable power systems is critical for both industrial and residential applications, and at the heart of these systems is the generator rotor. As a crucial component, the rotor plays a vital role in converting mechanical energy into electrical power.
Over time, however, wear and tear can lead to rotor issues, threatening the efficiency and reliability of the entire generator system. This comprehensive article explores expert solutions for generator rotor repair, highlighting common problems, professional techniques, and best practices to ensure your power systems remain operational and efficient.
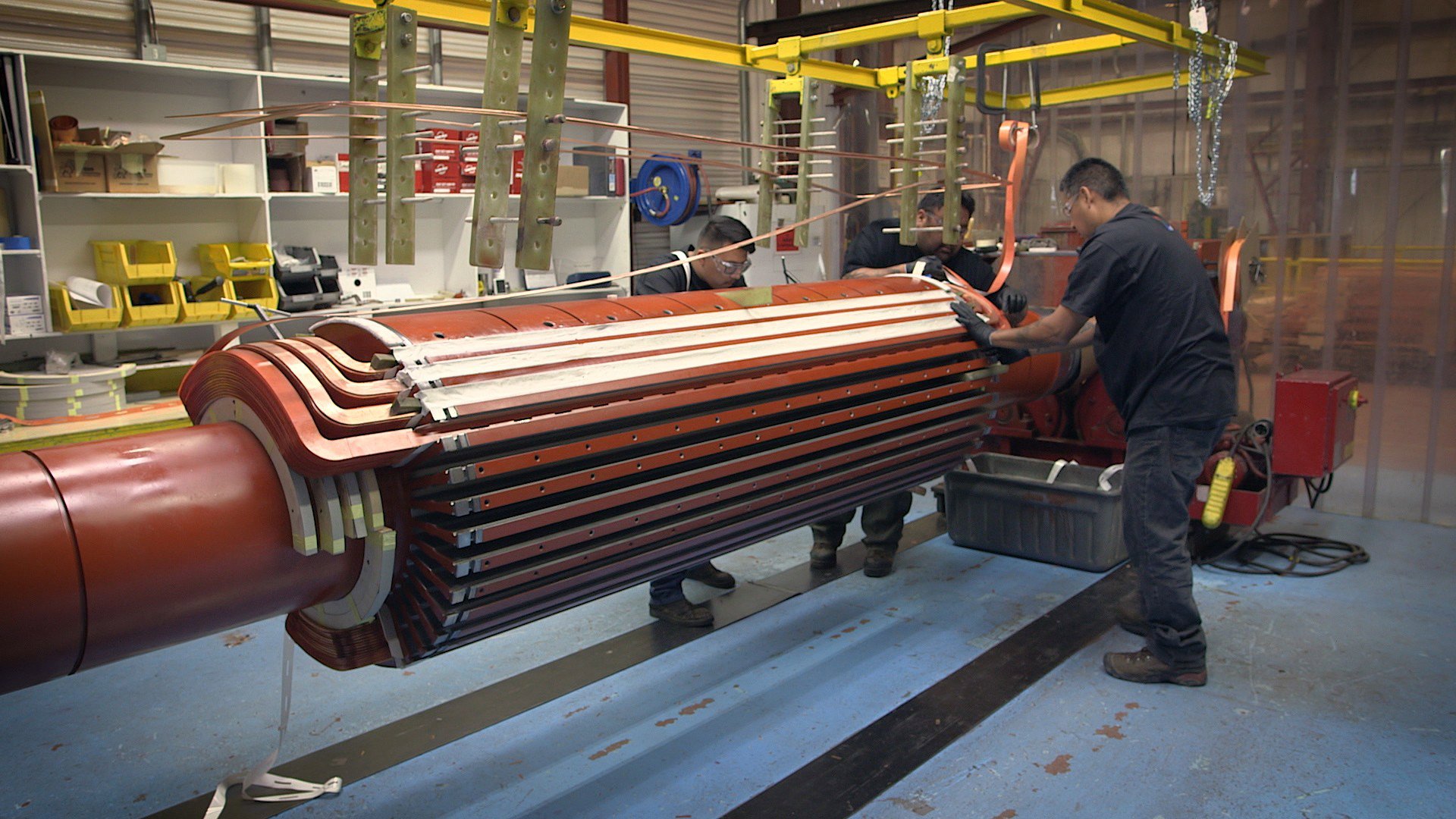
The generator rotor is the rotating part of the generator that interacts with the stator to produce electricity. It typically consists of a shaft, windings, and, in some designs, magnetic field components. The rotor’s movement generates a magnetic field that induces an electrical current in the stator windings, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Due to its continuous operation and critical function, the rotor is subject to significant mechanical and thermal stresses, making it prone to various types of damage and wear.
Professional generator rotor repair services are essential in diagnosing and rectifying these issues, preventing unplanned downtime and costly failures. These services utilize advanced diagnostic tools and specialized repair techniques to address rotor problems such as imbalances, winding damage, and shaft misalignment. By restoring the rotor’s balance, integrity, and operational efficiency, repair services help in maintaining consistent power output and prolonging the lifespan of the generator.
Moreover, they provide critical maintenance interventions that preserve the health of the entire generator system, ensuring uninterrupted power supply for industrial, commercial, and residential applications. In essence, generator rotor repair services are indispensable in safeguarding the functionality and performance of power generation systems, thereby supporting the operational stability of businesses and communities.
Common Generator Rotor Issues
Several problems can arise with generator rotors, each requiring specific repair techniques to address effectively. Here are some of the most common issues:
- Rotor Imbalance: Over time, deposits, dirt, or component wear can cause the rotor to become unbalanced. This imbalance leads to excessive vibrations, which can damage bearings and other generator components.
- Electrical Faults: Windings on the rotor can develop shorts or opens due to insulation breakdown, excessive heat, or mechanical damage. Electrical faults can lead to inefficient power generation and, in severe cases, total failure.
- Mechanical Wear: Bearings, couplings, and other moving parts of the rotor can wear out due to friction and operational stresses. This wear can cause misalignment, increased friction, and eventual mechanical failure.
- Rotor Shaft Issues: The rotor shaft is subjected to high torque and rotational forces, which can lead to bending, cracking, or misalignment over time.
- Thermal Degradation: Continuous operation and high loads can cause the rotor to overheat, degrading insulation and potentially leading to winding failures or thermal expansion issues.
- Corrosion and Contamination: Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or other contaminants can corrode the rotor components, affecting their performance and lifespan.
Professional Techniques for Generator Rotor Repair
Addressing generator rotor issues requires a combination of diagnostic expertise and specialized repair techniques. Here are some professional solutions commonly employed by experts in the field:
- Dynamic Balancing
- Objective: Restore rotor balance to eliminate vibrations.
- Process: Technicians use precision balancing machines to detect and correct rotor imbalances. Weights are added or material is removed from the rotor to achieve a balanced state, ensuring smooth operation and reducing stress on the generator components.
- Insulation Repair and Rewinding
- Objective: Restore electrical integrity of the rotor windings.
- Process: Damaged insulation is repaired or replaced, and if necessary, the rotor windings are completely rewound. This involves removing the old windings, preparing the core, and installing new wire windings with proper insulation to restore electrical performance and reliability.
- Bearing Replacement and Alignment
- Objective: Ensure smooth rotation and reduce friction.
- Process: Worn or damaged bearings are replaced, and the rotor is realigned to ensure proper fit and function. Alignment tools and techniques are used to achieve precise positioning, minimizing wear and improving operational efficiency.
- Shaft Repair and Machining
- Objective: Restore the structural integrity and alignment of the rotor shaft.
- Process: Techniques such as welding, grinding, or machining are used to repair cracks, bends, or other damage to the rotor shaft. This ensures the shaft is straight and capable of handling the operational stresses without failure.
- Thermal and Mechanical Analysis
- Objective: Identify and address issues related to heat and mechanical stress.
- Process: Thermal imaging, strain gauges, and other diagnostic tools are used to assess the rotor’s thermal performance and mechanical stresses. Based on this analysis, repairs or modifications are made to improve cooling, reduce stress concentrations, and prevent future failures.
- Surface Treatment and Coating
- Objective: Protect the rotor from corrosion and wear.
- Process: Surface treatments such as plating, coating, or painting are applied to the rotor components. These treatments protect against corrosion, reduce friction, and extend the lifespan of the rotor by providing a protective barrier against environmental and operational factors.
- Vibration Analysis and Monitoring
- Objective: Detect and address early signs of imbalance or mechanical issues.
- Process: Advanced vibration monitoring systems are installed to continuously track the rotor’s performance. This data helps in early detection of imbalances or other mechanical issues, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing major failures.
- Laser Cladding and Metal Spraying
- Objective: Repair and restore rotor components with precision.
- Process: Laser cladding and metal spraying techniques are used to add material to worn or damaged areas of the rotor. These methods provide precise control over the deposition process, ensuring high-quality repairs that restore the rotor to its original specifications.
Best Practices for Generator Rotor Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial to extend the lifespan of generator rotors and avoid unexpected breakdowns. Here are some best practices recommended by professionals:
- Routine Inspections: Perform regular visual and technical inspections to detect early signs of wear, imbalance, or electrical issues. Pay attention to unusual noises, vibrations, or temperature changes that could indicate underlying problems.
- Vibration Monitoring: Implement continuous vibration monitoring systems to keep track of rotor balance and alignment. This helps in identifying imbalances early and scheduling corrective actions before they cause significant damage.
- Temperature Control: Ensure adequate cooling and ventilation for the generator. Overheating can lead to thermal degradation of components, so maintaining proper temperature control is essential.
- Lubrication and Cleaning: Regularly lubricate bearings and other moving parts to reduce friction and wear. Keep the rotor and surrounding components clean to prevent contamination and corrosion.
- Alignment Checks: Periodically check and correct the alignment of the rotor and other critical components. Misalignment can cause excessive wear and operational inefficiencies.
- Electrical Testing: Conduct routine electrical tests to ensure the integrity of the windings and insulation. This includes resistance measurements, insulation testing, and checking for shorts or opens in the circuits.
- Documentation and Records: Keep detailed records of all maintenance activities, inspections, and repairs. This documentation helps in tracking the rotor’s condition over time and planning future maintenance effectively.
Choosing the Right Professional for Rotor Repair
Selecting a qualified and experienced professional to handle rotor repairs is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of your generator. Consider the following factors when choosing a repair service:
- Experience and Expertise: Look for professionals with extensive experience in generator rotor repair. Their expertise in handling various rotor issues and familiarity with different generator models ensures effective and reliable repairs.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools: Ensure the service provider uses advanced diagnostic tools and techniques for accurate assessment and repair of rotor issues. This includes vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and precision balancing equipment.
- Quality Assurance: Choose a service that prioritizes quality assurance and follows industry standards for repairs. They should use high-quality materials and components to ensure lasting repairs.
- Customer Reviews and References: Check customer reviews and ask for references to gauge the service provider’s reputation and track record. Positive feedback and testimonials indicate reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Comprehensive Services: Opt for a provider that offers a comprehensive range of services, from diagnostics and repairs to preventive maintenance and monitoring. This ensures they can handle all aspects of rotor maintenance and repair.
- Responsive and Reliable: Select a service that is responsive to your needs and provides timely support. Quick turnaround times and reliable service are essential for minimizing downtime and maintaining operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Generator rotors are integral to the reliable operation of power systems, and maintaining their efficiency through expert repair and maintenance is crucial. By understanding common rotor issues, employing professional repair techniques, and adhering to best maintenance practices, you can keep your power systems running smoothly and extend the lifespan of your generator. Whether you’re dealing with imbalances, electrical faults, or mechanical wear, choosing the right professional service ensures that your generator rotor is restored to optimal condition, providing dependable power for years to come.